Structural BIM Modeling: A Game-Changer for Modern Building Design and Engineering
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital modeling technique used in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry to create 3D models of buildings and infrastructure. Structural BIM is specifically focused on the structural engineering aspect of BIM, providing comprehensive and accurate digital models of the building's structural components. This article will explore the introduction, advantages, and applications of structural BIM modeling.
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
3D Model of Building Structure uses advanced software tools to create detailed models of building structures. The models are created using intelligent objects that are parametrically designed, which means that they can be easily edited and updated. These models can also be integrated with other BIM models, such as architectural and MEP models, to create a comprehensive digital model of the building.
Structural Design includes the creation of 3D models of structural elements such as columns, beams, walls, slabs, foundations, and trusses. These models are typically used for structural analysis, construction documentation, and construction coordination.
[edit] Advantages
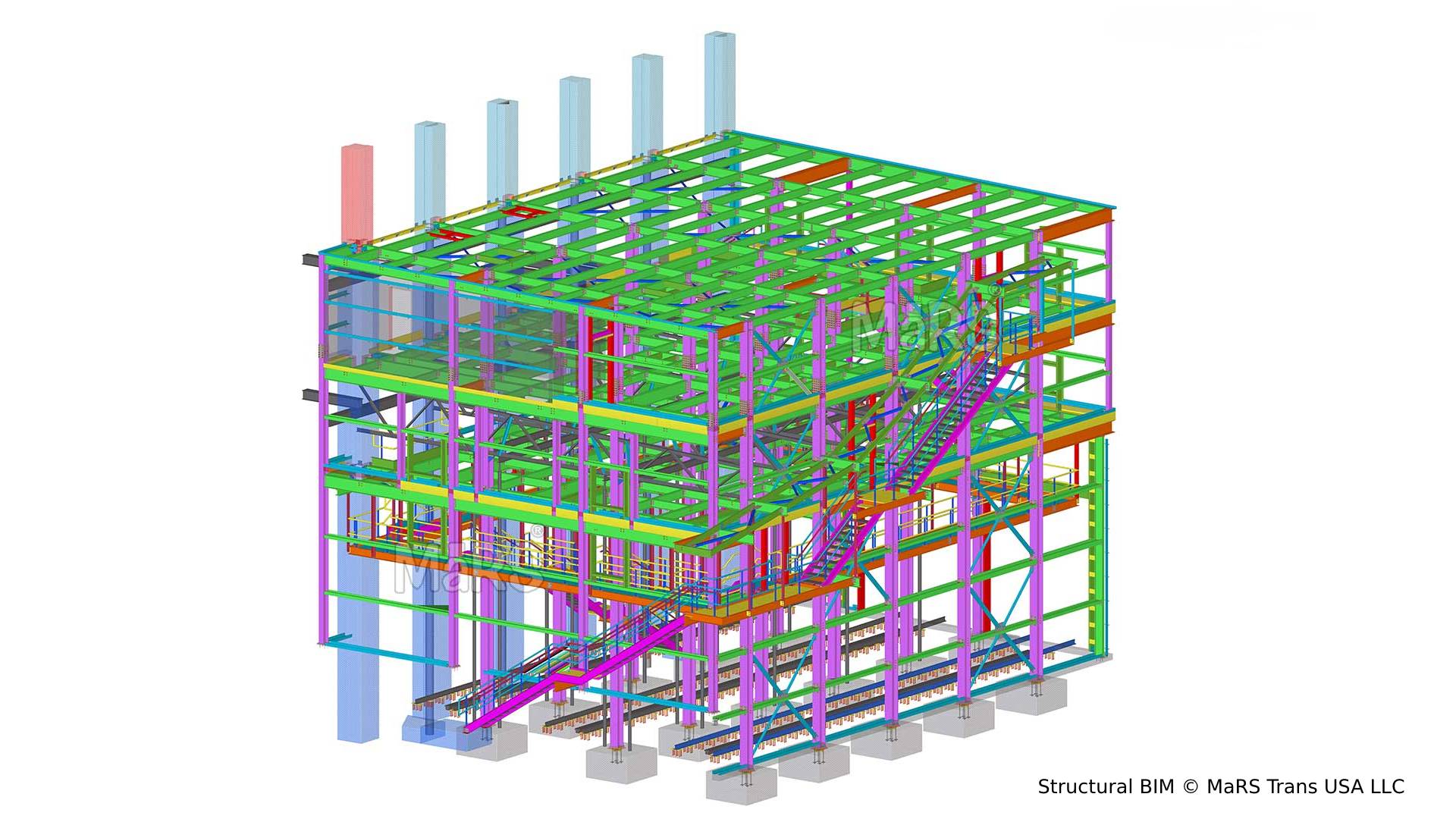 Advance Structural BIM offers Several Advantages over traditional 2D CAD drawings and manual calculations. Here are some of the key advantages:
Advance Structural BIM offers Several Advantages over traditional 2D CAD drawings and manual calculations. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Accuracy: Structural Models provide highly accurate models that are based on real-world conditions. This accuracy helps to reduce errors and omissions during construction, which can save time and money.
- Coordination: BIM Models allow for better coordination between different trades and disciplines, which helps to avoid conflicts and reduces rework.
- Visualization: BIM models provide a 3D visualization of the building structure, which can help to improve communication between stakeholders and make it easier to understand the design intent.
- Analysis: Structural BIM models can be used for structural analysis, allowing engineers to test different scenarios and optimize the design for better performance.
- Cost savings: By using BIM models, construction teams can reduce waste and optimize resources, which can result in significant cost savings.
[edit] Applications
 3D Structural engineers are used in a wide range of construction projects, including commercial buildings, residential buildings, industrial facilities, and infrastructure projects.
3D Structural engineers are used in a wide range of construction projects, including commercial buildings, residential buildings, industrial facilities, and infrastructure projects.
Here are some of the common applications of Structural BIM:
- Structural analysis: BIM models can be used for structural analysis, allowing engineers to simulate different scenarios and optimize the design for better performance.
- Construction documentation: BIM models can be used to create detailed construction documentation, including structural drawings, steel detailing drawings, specifications, and bills of materials.
- Clash detection: BIM models can be used for clash detection, which helps to identify potential conflicts between different trades and disciplines.
- Coordination: BIM models can be used to coordinate different aspects of construction, including scheduling, sequencing, and resource allocation.
- Facility management: BIM models can be used for facility management, allowing building owners and operators to manage and maintain their facilities more efficiently.
[edit] Conclusion
3D Structural BIM offers several advantages over traditional 2D CAD drawings and manual calculations. They provide accurate, coordinated, and visual models that can be used for structural analysis, construction documentation, and construction coordination. With the increasing adoption of BIM in the AEC industry, Structural 3D BIM is becoming essential for modern construction projects.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Asset information requirements AIR.
- BIM articles.
- BIM maturity levels.
- BIM resources.
- Building drawing software.
- Building information modelling BIM.
- Construction Operations Building Information Exchange (COBie).
- Collaborative practices.
- Common data environment.
- Data drops.
- Digital engineering.
- Digital information.
- Digital model.
- Federated building information model.
- Government Construction Strategy.
- Government Soft Landings.
- Improving health and safety using BIM.
- Industry Foundation Classes.
- Information management.
- Information manager.
- Level of detail.
- MEP BIM and the building lifecycle.
- NBS Chorus.
- NBS National BIM Report 2020.
- PAS 1192-2:2013.
- PAS 1192-3:2014.
- Revit.
- Soft landings.
- Uniclass.
BIM Directory
[edit] Building Information Modelling (BIM)
[edit] Information Requirements
Employer's Information Requirements (EIR)
Organisational Information Requirements (OIR)
Asset Information Requirements (AIR)
[edit] Information Models
Project Information Model (PIM)
[edit] Collaborative Practices
Industry Foundation Classes (IFC)






